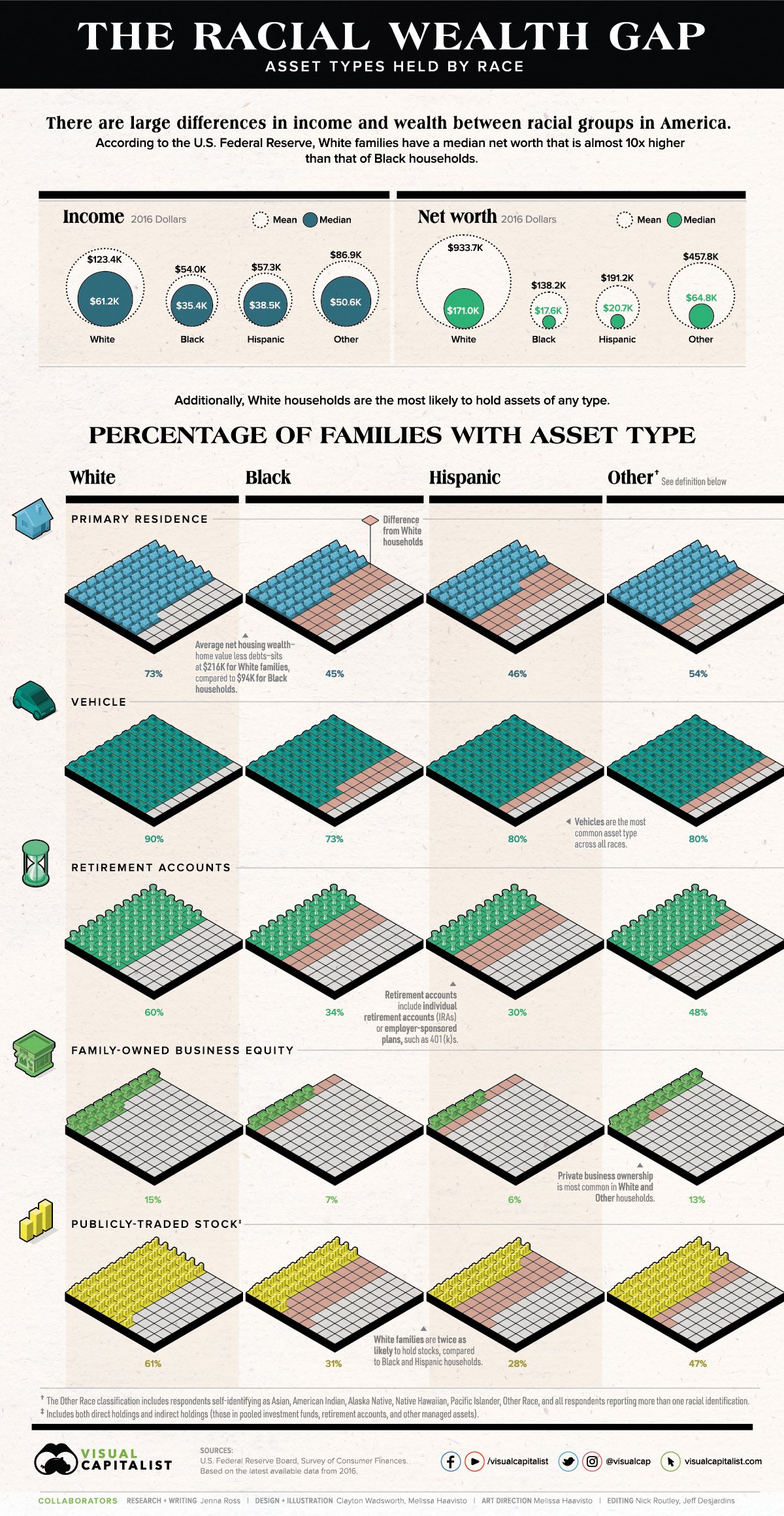
You’ve heard it before. We see what we want to see. It’s called confirmation bias, and we are all susceptible. Confirmation bias is a big problem to those presenting or consuming data (i.e. all of us.) How can we draw our own and others’ attention to the data that does NOT fit our existing beliefs? How, in other words, can we check our blind spots?
The great thing about your blind spot when it comes to driving is that you know it exists. Your rearview mirrors do not show you an area next to and behind your car. So you learn to check that area in a different way. Experienced drivers do it by rote. Wouldn’t it be great if we also could remember that we have data blind spots and learn to check them automatically?
Here are some ideas for making your blind spots visible. All of them involve doing something before you look at data (in the form of a spreadsheet, table, chart, map, or graph) to help you look at the data with fresh eyes.
Make predictions before looking at data. To prevent seeing only the data that confirm our beliefs, we can make predictions before looking at the data. In Staff Making Meaning from Evaluation Data, Lenka Berkowitz and Elena “Noon” Kuo suggest that, before sharing data with program staff, “have them spend 10 minutes writing down predictions about what the data will say. This exercise helps surface beliefs, assumptions, and biases that may otherwise remain unconscious.” This can involve drawing a predicted trend in the data or jotting down guesstimates of key data points. Then look for differences between your predictions and the actual data and consider:
What may have contributed to the differences,
What more do you need to know to take action, and
What actions might you consider immediately?
Consider your “null hypothesis” before looking at data. This approach is a variation on strategy number one. Rather than making a prediction, you pose this question to yourself: If what I expect is NOT true, what might I see? This is analogous to how researchers conduct experiments. Rather than trying to prove that a hypothesis (e.g. A is affecting B) is correct, researchers aim to collect sufficient evidence to overturn the presumption of no effect, otherwise known as the null hypothesis. It’s sort of like innocent until proven guilty. The idea is to take the opposite view to the one that you hold and then look for evidence to support it. If you can’t find that evidence, then your assumption might be correct. This approach makes you think more critically and perhaps more dispassionately when encountering data.
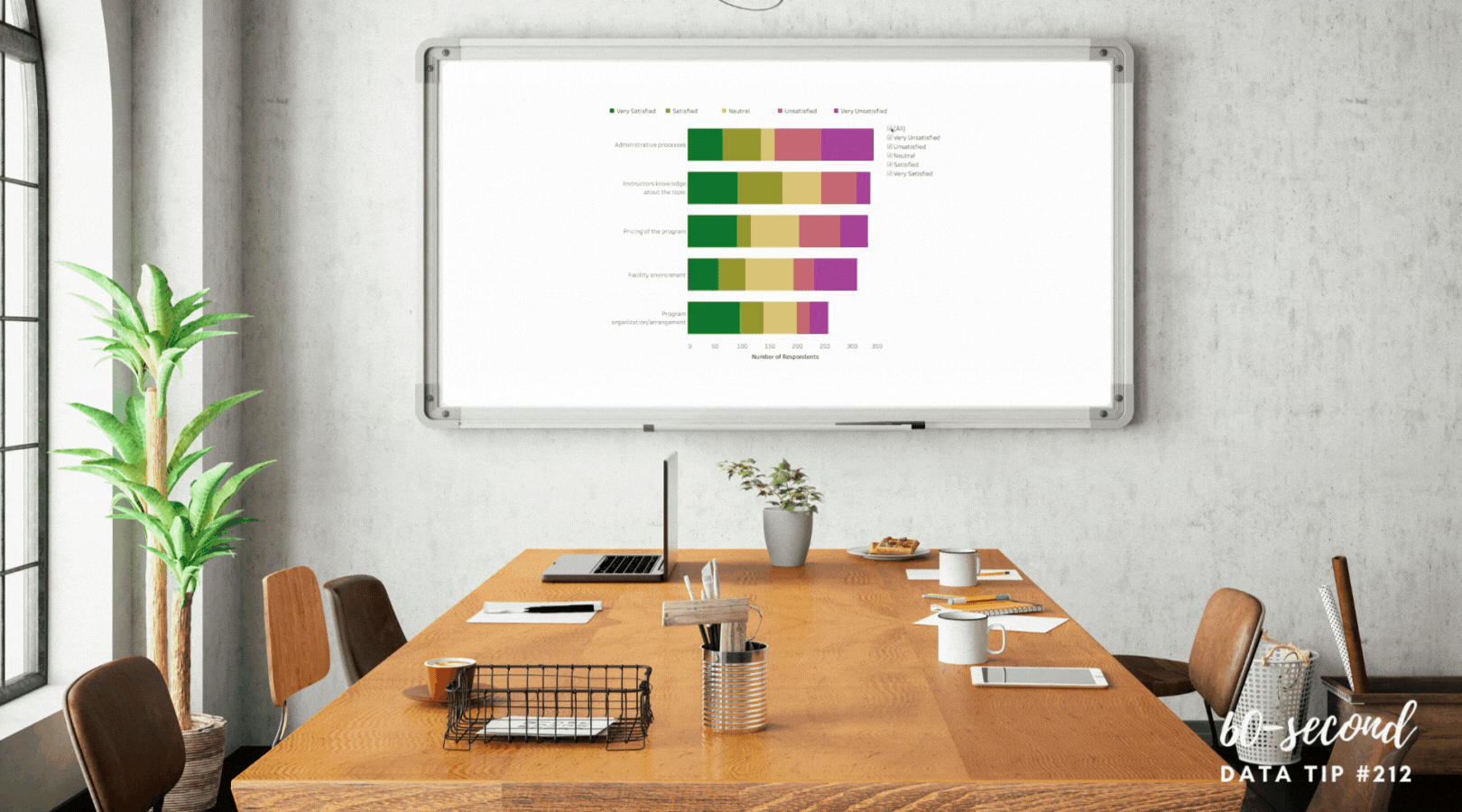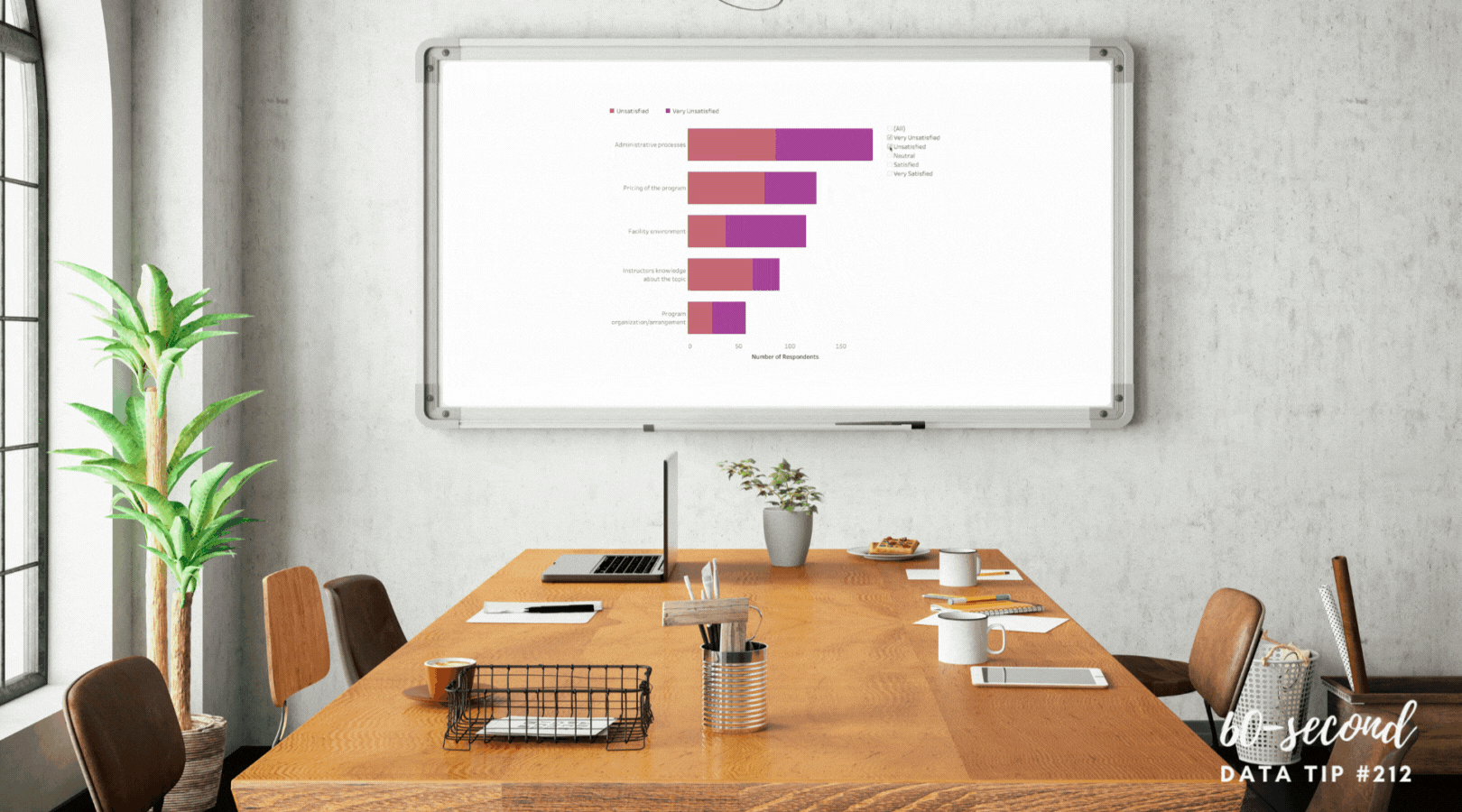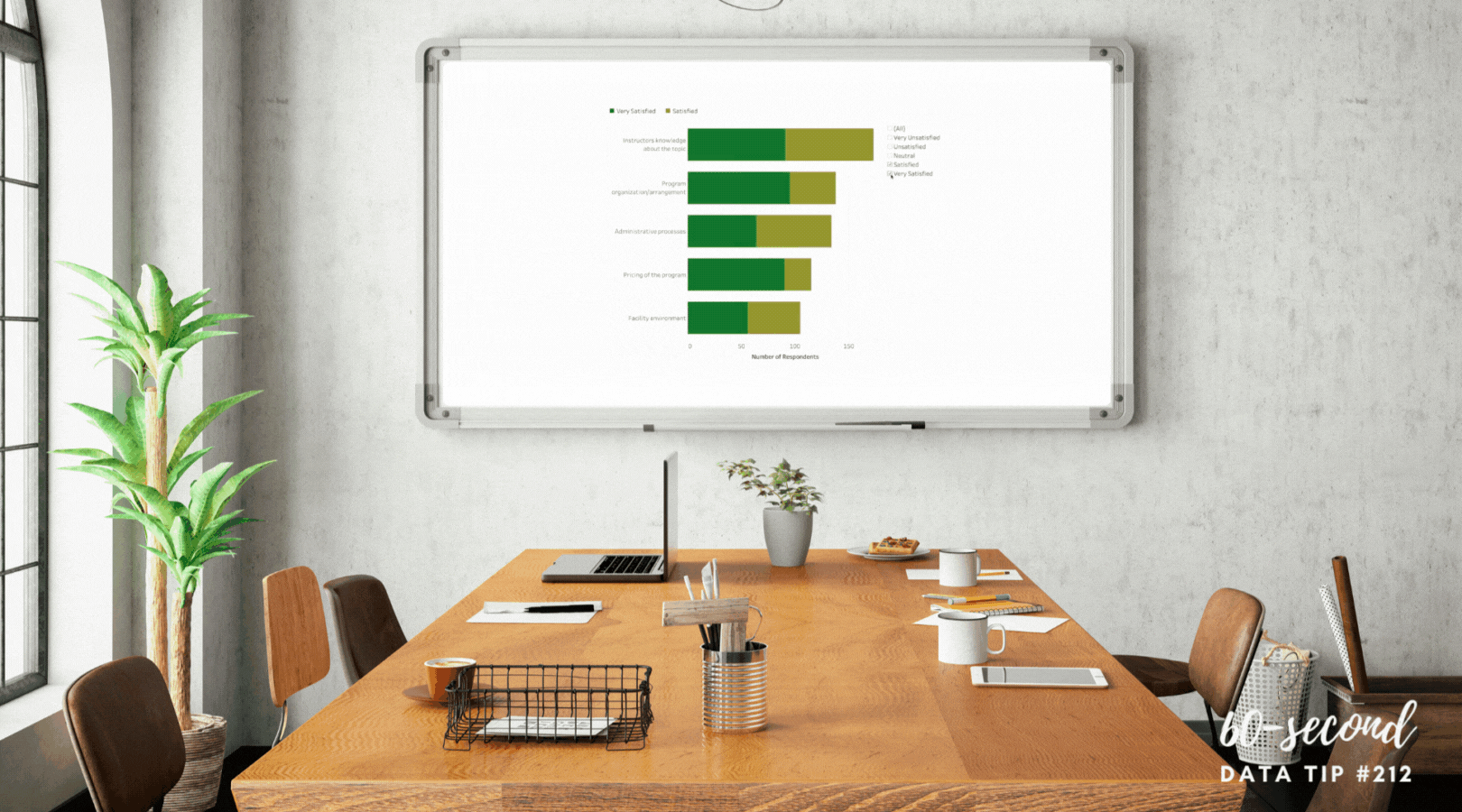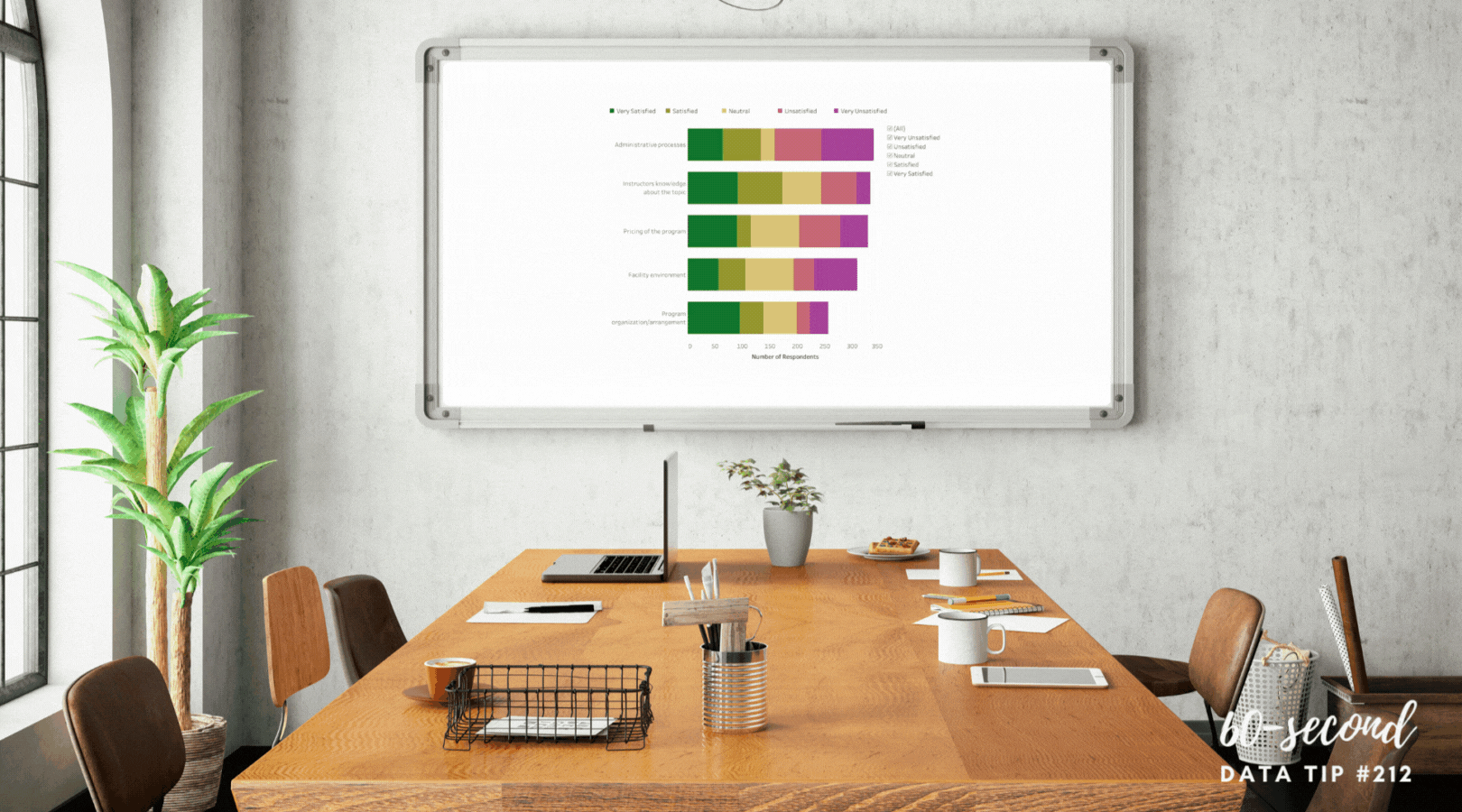
Set decision criteria before looking at data. “Many people only use data to feel better about decisions they’ve already made,” notes Cassie Kozyrkov in Data-Driven? Think again. To avoid this, you can frame your decision-making in a way that prevents you from moving the goalposts after you’ve seen where the ball landed. Before considering the data, determine your cutoffs for action. For example, you and your colleagues might decide that program participation below 150 in any given month requires investigation and possible action. Let’s say that twelve-month data show participation below 150 in six months. The pre-established cutoff can prevent you from only focusing on the worst months when participation was below 75.
Let’s talk about YOUR data!
Got the feeling that you and your colleagues would use your data more effectively if you could see it better? Data Viz for Nonprofits (DVN) can help you get the ball rolling with an interactive data dashboard and beautiful charts, maps, and graphs for your next presentation, report, proposal, or webpage. Through a short-term consultation, we can help you to clarify the questions you want to answer and goals you want to track. DVN then visualizes your data to address those questions and track those goals.