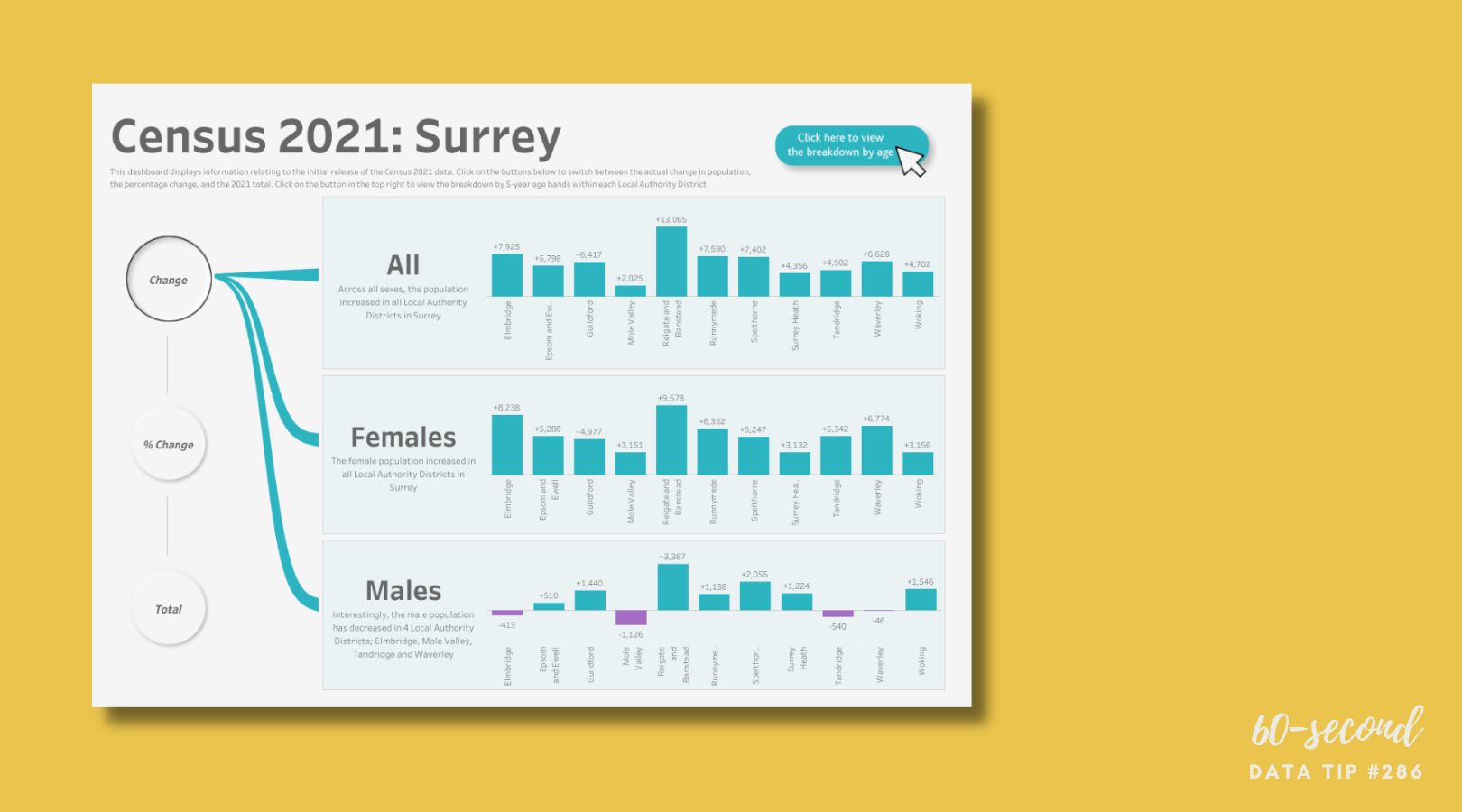
Reposted from July 2023
This “sketchplanation” elegantly demonstrates the importance of context in understanding anything. Since data visualizations are supposed to help people understand something, we should pay close attention to context when creating them, adding as much context as is needed for others to appreciate what’s going on and act on it. Considering the following charts . . .
Low-context chart
This is your garden variety chart. I see them all the time. Sure, it provides some context by comparing clients served in different zip code areas. But it doesn’t give me enough context to understand if these numbers are high, low, or somewhere in between. This chart needs more context.
Moderate-context chart
This chart is better than the one above. By providing the previous year’s numbers, we can see where there has been increases and decreases and how large and small they were as well as compare the number increases (3) to the number of decreases (1).
Moderate-context chart
This chart, too, allows for better assessment of the numbers than the first chart did. By simply adding a reference line for the goal, we have a better understanding of what’s going on and where we might need to take action. A reference line showing the average number of clients per zip code might also be helpful.
High-context chart
This “small multiples chart”* gives us much more context by showing how the current numbers compare to past years. Consider, for example, the trend for 60601. Just knowing the current and past years’ numbers would not give you an appreciation of the overall upward trend.
*Small multiples chart: a series of similar graphs or charts using the same scale and axes, allowing them to be easily compared
Let’s talk about YOUR data!
Got the feeling that you and your colleagues would use your data more effectively if you could see it better? Data Viz for Nonprofits (DVN) can help you get the ball rolling with an interactive data dashboard and beautiful charts, maps, and graphs for your next presentation, report, proposal, or webpage. Through a short-term consultation, we can help you to clarify the questions you want to answer and goals you want to track. DVN then visualizes your data to address those questions and track those goals.