Reposted from June 2018
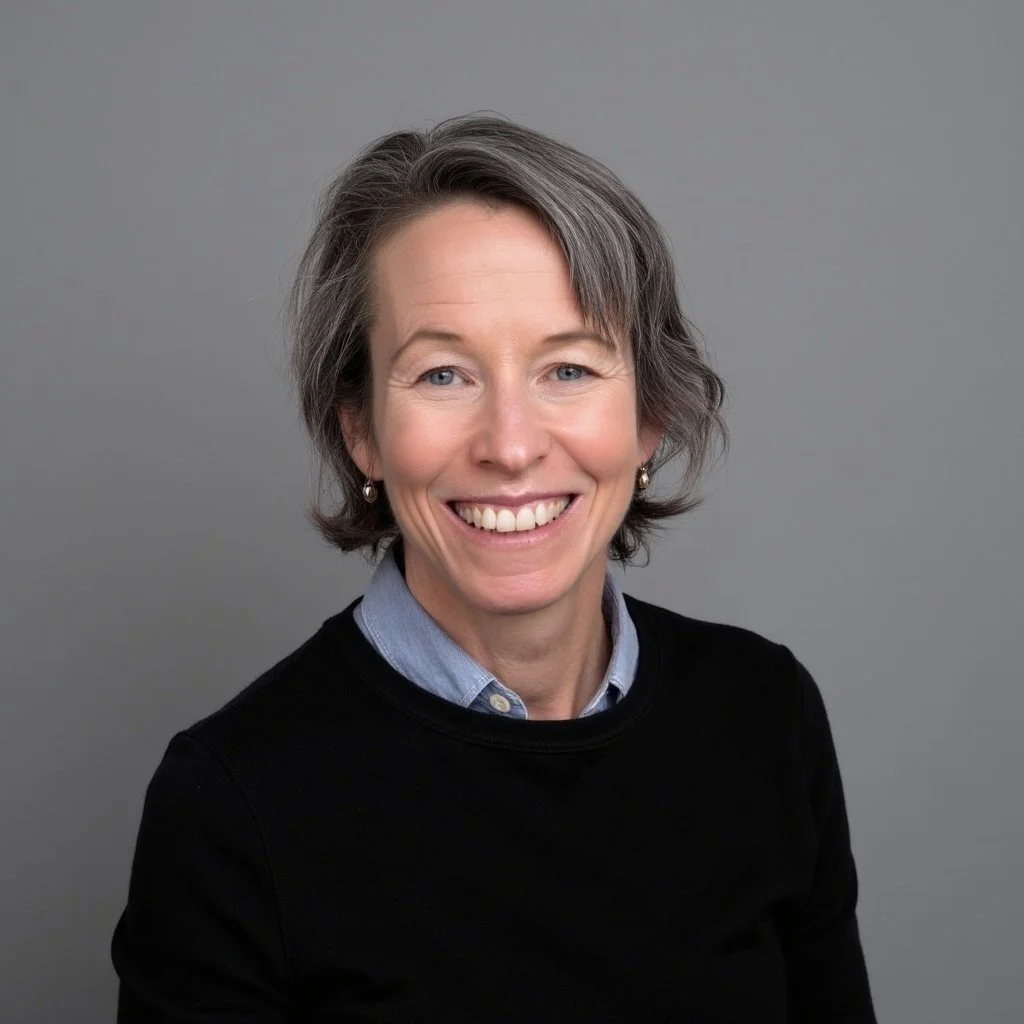
Pretend that you are Goldilocks and your porridge is data. How much data is just right? Just enough to engage your funders, staff, or board members, but not so much as to be overwhelming?
To answer this question, we might consider Miller’s Law. George A. Miller was a psychology professor at Princeton University and wrote one of the most frequently cited papers in psychology: "The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information."
Miller conducted experiments on human memory and concluded that the number of objects that an average human can remember in the short-term is 7 ± 2. Objects can include symbols like numbers or abstract concepts. We also can hold several groups of related objects in mind.
Armed with this knowledge, we can make visualizations of data (charts, maps, graphs) easier to digest by:
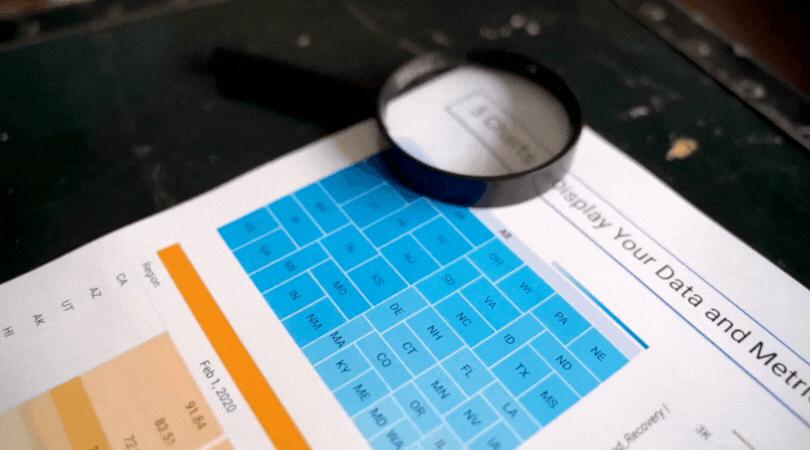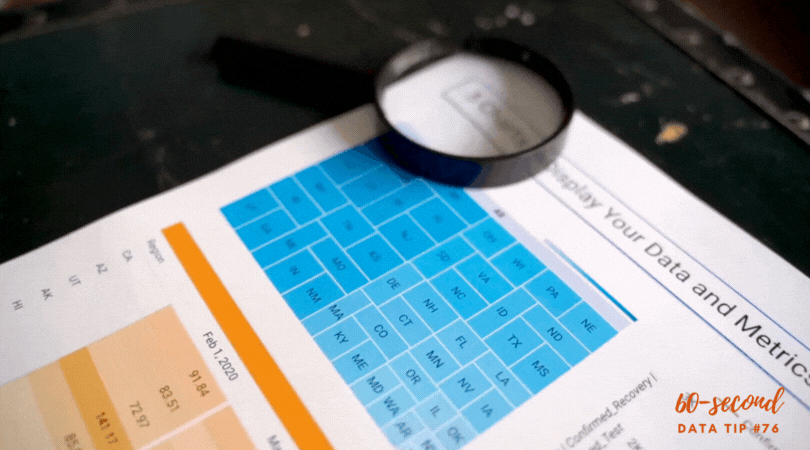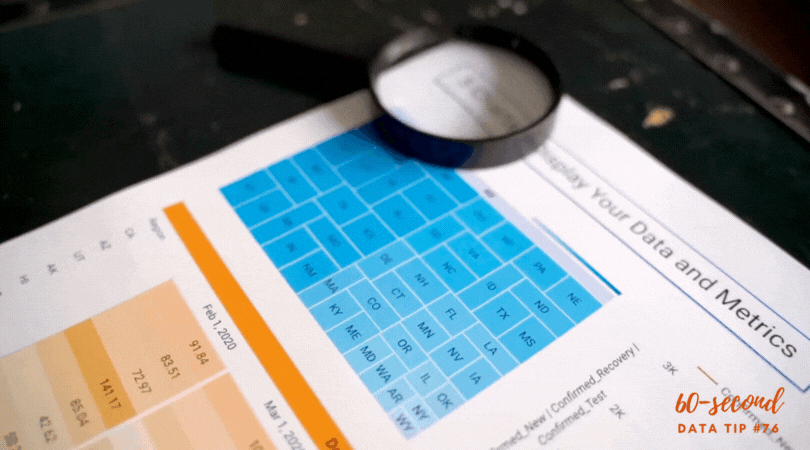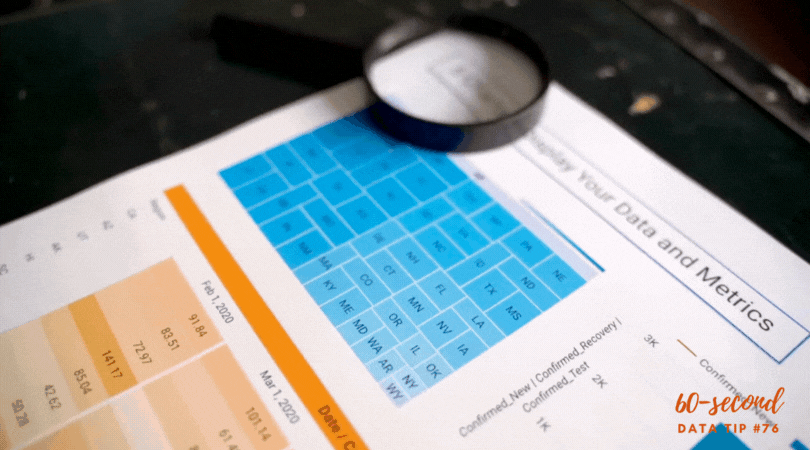
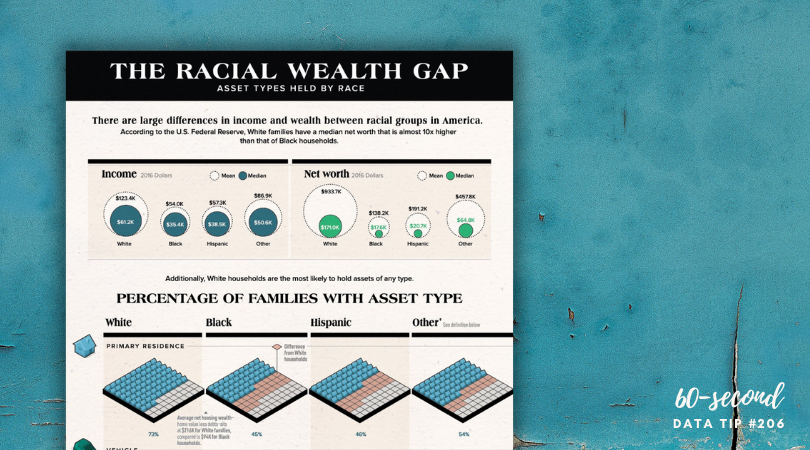
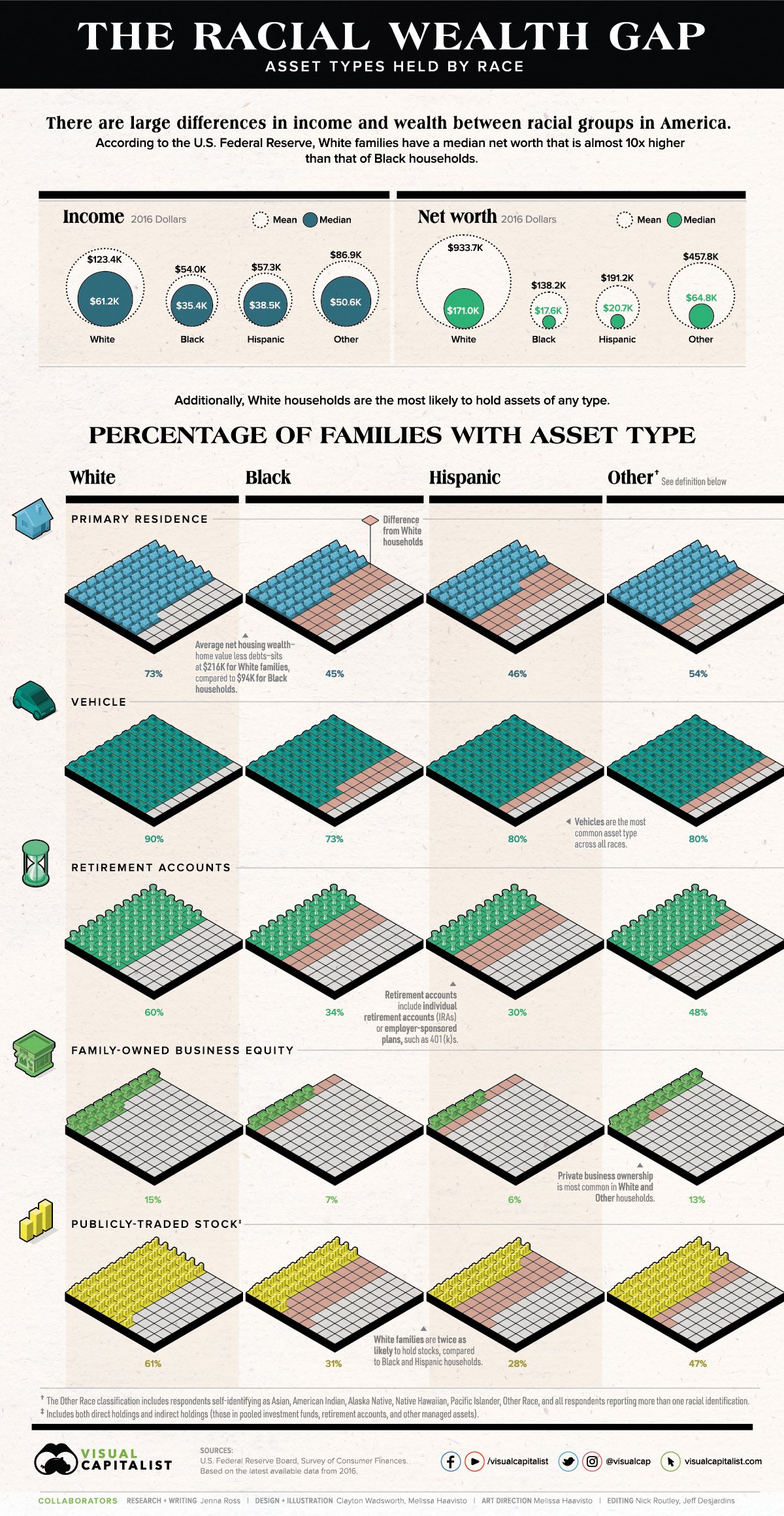
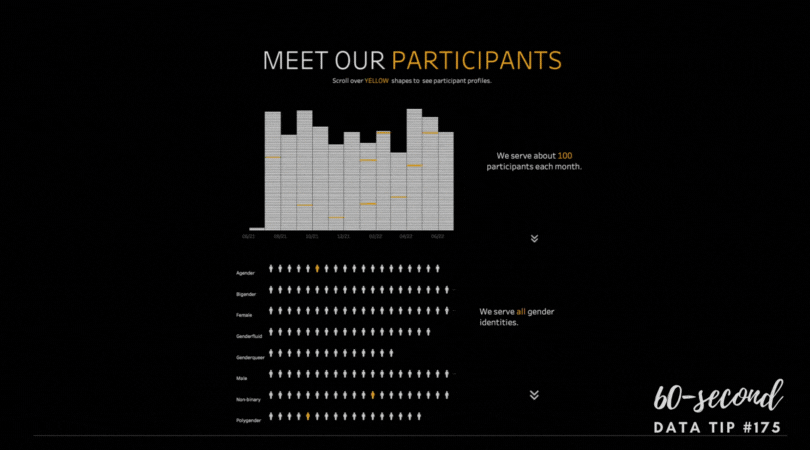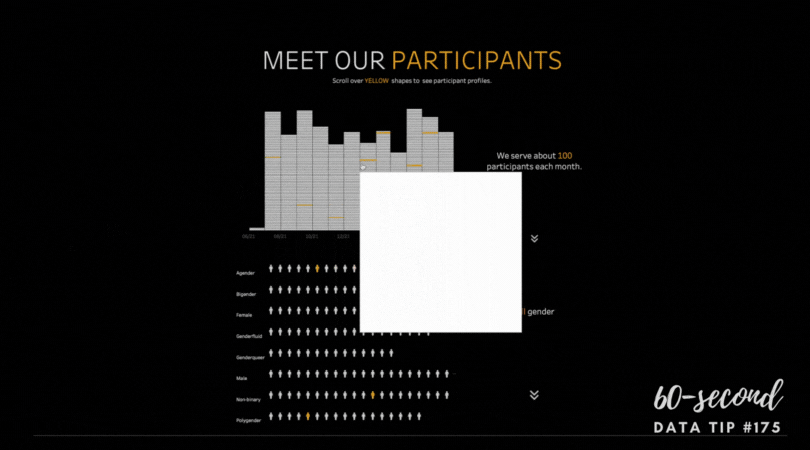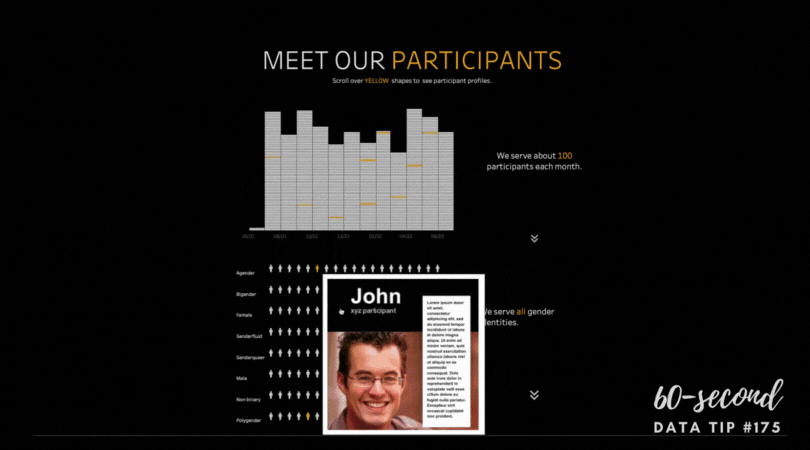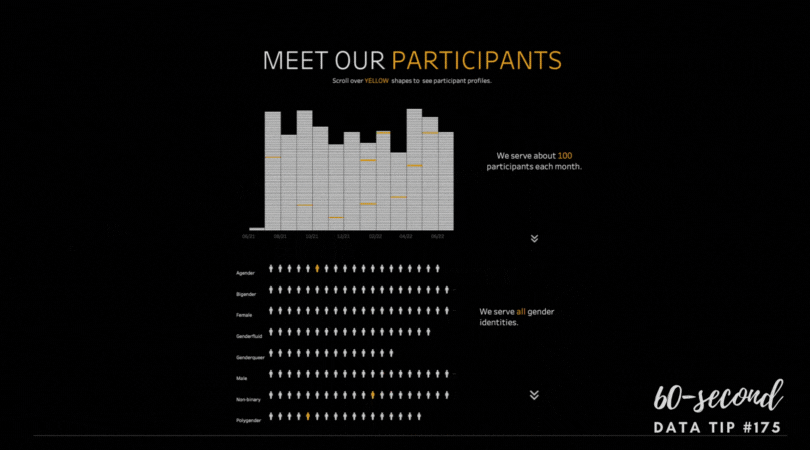
1) Grouping data into categories. Whenever you have a graph or chart with more than 5 data categories, the individual units start to lose their individuality and are perceived by our eyes as a single whole. In the “before” and “after” examples below, the after chart is easier to process because it combines data on donors into just two groups: those in Chicago and those in other cities.
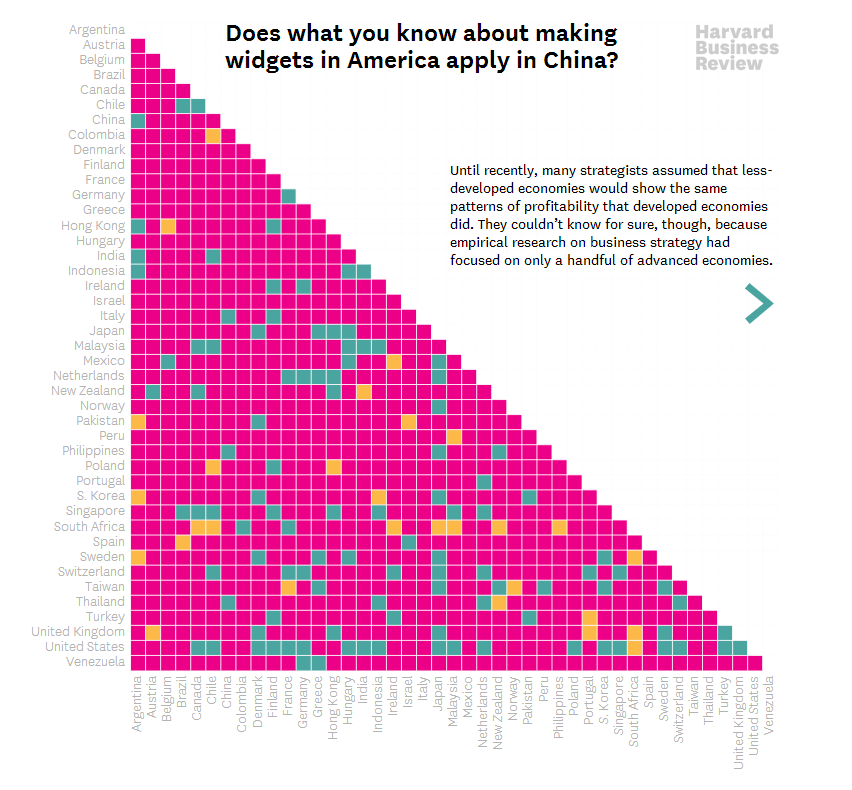
2) Highlight one or two single categories and gray out the rest. The second chart below (called a parallel coordinates chart) includes a line for each of the 50 states showing the prevalence of various diseases in each state. But only one state (Hawaii) is highlighted and the rest are grayed out. Thus there are really only two data categories to compare: 1) Hawaii and 2) the rest of the states.
BEFORE: TOO MANY GROUPS
AFTER: JUST TWO GROUPS
HIGHLIGHT ONE GROUP
Let’s talk about YOUR data!
Got the feeling that you and your colleagues would use your data more effectively if you could see it better? Data Viz for Nonprofits (DVN) can help you get the ball rolling with an interactive data dashboard and beautiful charts, maps, and graphs for your next presentation, report, proposal, or webpage. Through a short-term consultation, we can help you to clarify the questions you want to answer and goals you want to track. DVN then visualizes your data to address those questions and track those goals.